The purpose of this section is to provide an overview of the technical aspects of micro web applications (MWA), domain model and integration contracts between web and native application parts. Understanding the MWA architecture is essential for engineers working with the technology, as it allows them to make informed decisions about how to design and implement applications and ensure that they function properly.
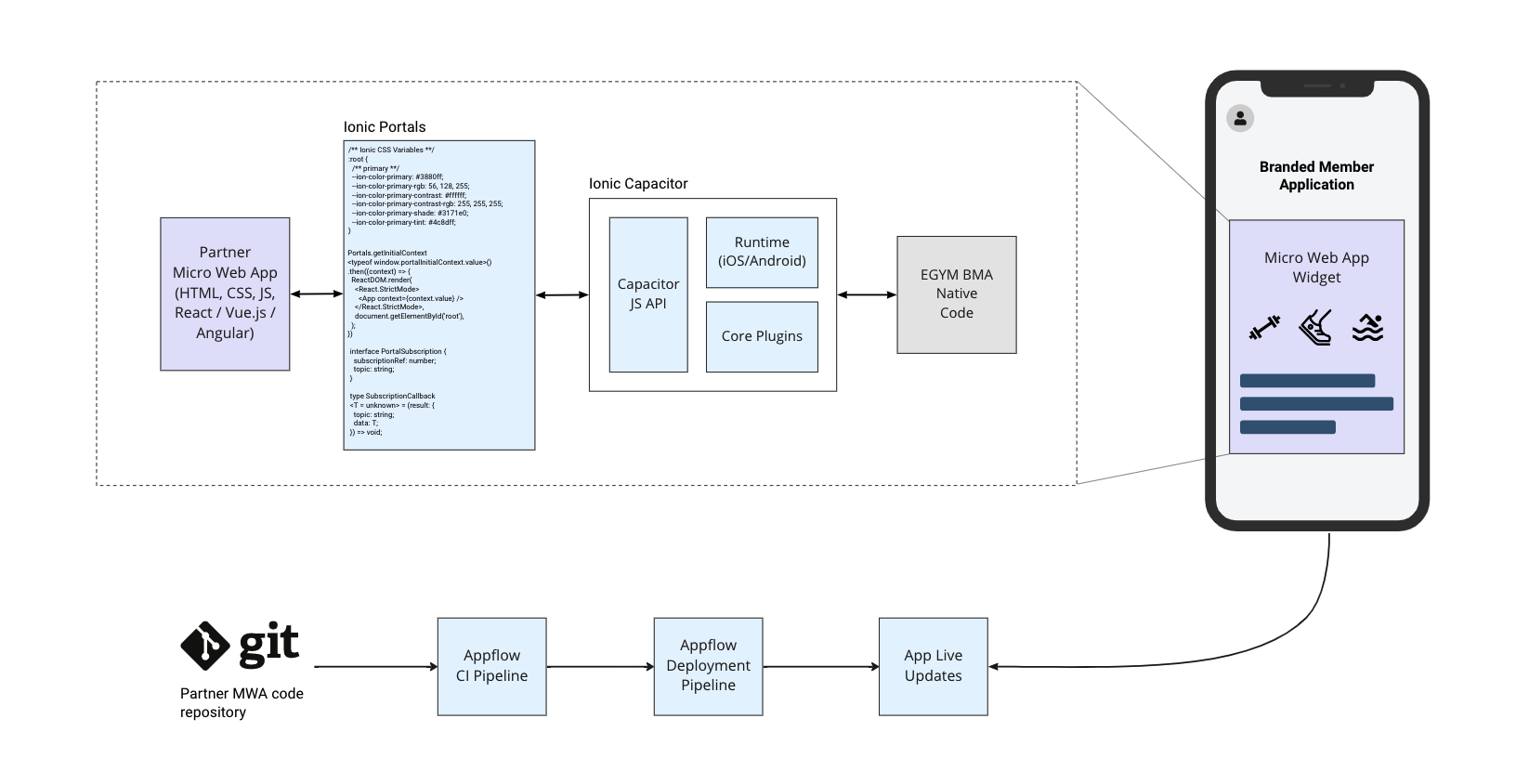
Micro Web Applications are powered by a number of components developed by Ionic company, namely:
- Capacitor runtime as a bridge between web and native application parts
- Capacitor plugins (e.g. Camera, Geolocation, HTTP Client) to access native features and connect to partner backends
- Ionic Portals framework to render web content and provide seamless interoperability with native application
- Appflow as CI and deployment platform
- Live Updates as transport for delivering web builds directly to user devices without the need of publishing new versions of mobile applications.
In this part of the documentation we are going to focus on integration contracts and communication mechanisms provided by Capacitor bridge and plugins. Information about use of Ionic Appflow and Live Updates can be found in Development Process section, and details about work with Ionic Portals framework are covered in Getting Started with MWA page.
One of the first steps in creating a new Micro Web Application on the EGYM BMA platform is to decide where the application should become visible. EGYM offers a flexible configuration framework that allows the insertion of links to the web application into multiple places in the mobile application.
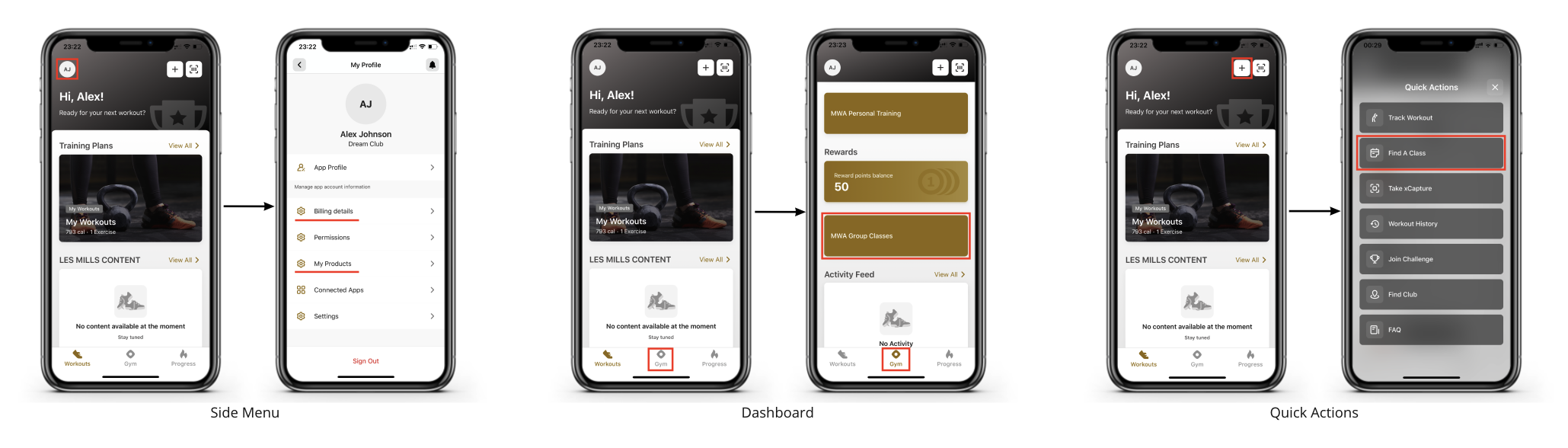
As shown in the diagram below it is possible to add links to the following BMA components:
Side menu. This is a side menu control that provides access to the user profile, user membership details, preferences, and application settings. Web application developers should also consider adding user-related configurations or preferences here
Main Dashboard. BMA provides capabilities to add features on different app screens which can be accessed using the toolbar at the bottom of the app. Each screen can show multiple items, and each item represents an entry point to a specific app feature. It is recommended to place related features together to provide a better experience to application users. Web applications launched this way are usually opened in fullscreen mode, but it is also possible to display them as pop-up widgets which appear in front of the main screen
Quick Actions menu. This menu provides an alternative way to access application features that are used often and can be considered as a shortcut to dashboard items.
Partners need to discuss with EGYM design and engineering teams where a particular web application should be placed and follow the recommendations provided by EGYM to avoid possible conflicts or misconfiguration of other application features.
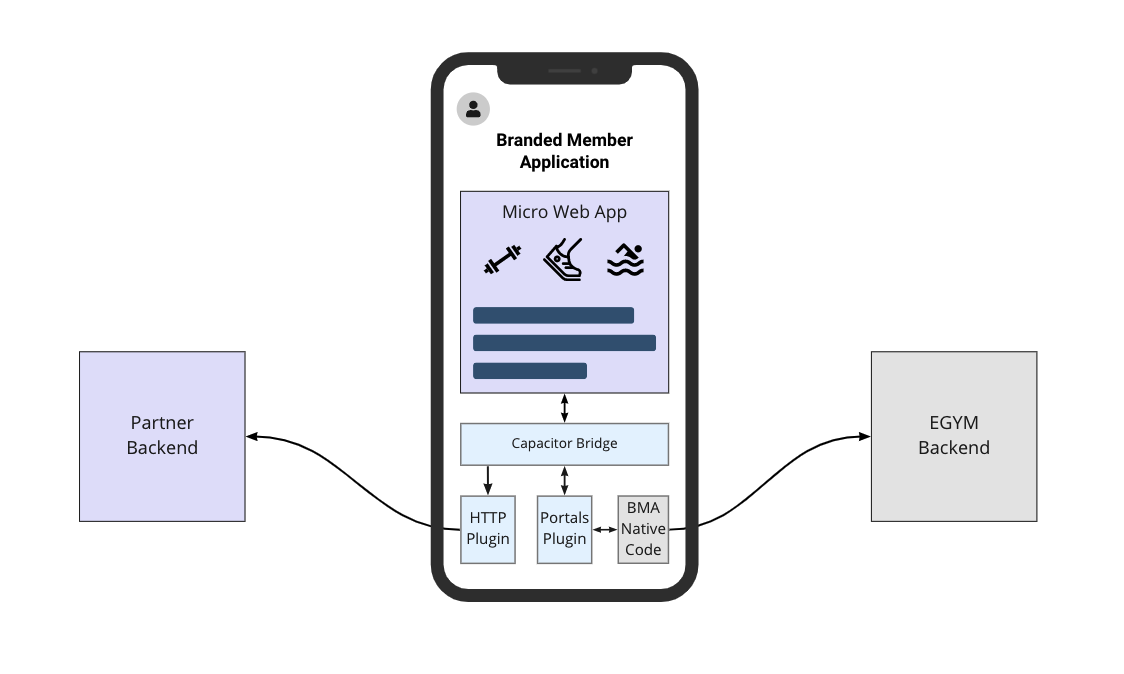
The diagram above illustrates how web app features can be integrated with EGYM platform and partner backends
All communication happens through a JavaScript API provided by Ionic Capacitor and Capacitor Plugins
Interaction with native app features such as camera, keyboards, device geolocation, and in-app navigation is handled by the respective Capacitor Core plugins. EGYM engineering maintains the list of plugins exposed to the web app to cover common use cases such as access to the camera or the geolocation
Access to EGYM data and the backend is handled by a Portals Plugin which provides a bidirectional asynchronous API based on the publish/subscribe model. A list of supported messages and data that can be sent over the Portals Plugin is maintained by EGYM engineeringand is described here
Access to external systems can be accomplished via Capacitor HTTP plugin. This plugin allows access to the native HTTP client and sends requests on behalf of the mobile app to partner backends. In order to provide a secure way of communication and identify requests made by a web app, EGYM provides capabilities to obtain identity tokens for authenticated app users. More details on using these tokens are provided here
Integration options can be summarized like this:
Access to EGYM platform and data is controlled and limited by contracts exposed through native interfaces and supported Ionic plugins
EGYM defines a public user data model that is exposed to the web application and can be shared with partner systems
Web applications can access any API exposed by partner backends to update application specific data, but it is important to ensure that all requests are properly secured and scoped to a user identified by tokens provided by EGYM.
There are more plugins available and maintained by both Ionic development team and Capacitor community. However, only the plugins listed above are supported and available in the EGYM app platform at this point.
Initial Context can be used to provide a web app with a set of data before it is initialized and shown to a user. An example of such data can be the application configuration (e.g. URL of MWA backend or colors scheme used by web application) or the identity token used to represent authenticated app user.
The data provided in the initial context is structured as a dictionary (json object) with values of string type or nested json objects.
The list of passed attributes are described here
Portals Plugin allows bidirectional communication between web and native application parts through a lightweight message broker with pub/sub semantics. The API provides capabilities to publish request messages to a particular topic and register a callback function to consume response data sent to that topic.
This approach is recommended for exchanging data between native and web application parts (e.g. retrieving exerciser profile details or authentication tokens) and also for cases when the web application needs to trigger an execution of certain behavior in a native app (such as navigation to a certain feature or opening a web view).
All communication between web and native applications is organized by sending commands. Web application starts communication by sending requests to the topic called subscription and waits for a reply by subscribing to a reply topic. The native application receives the request, processes it depending on the type of sent command and publishes a response to the reply topic.
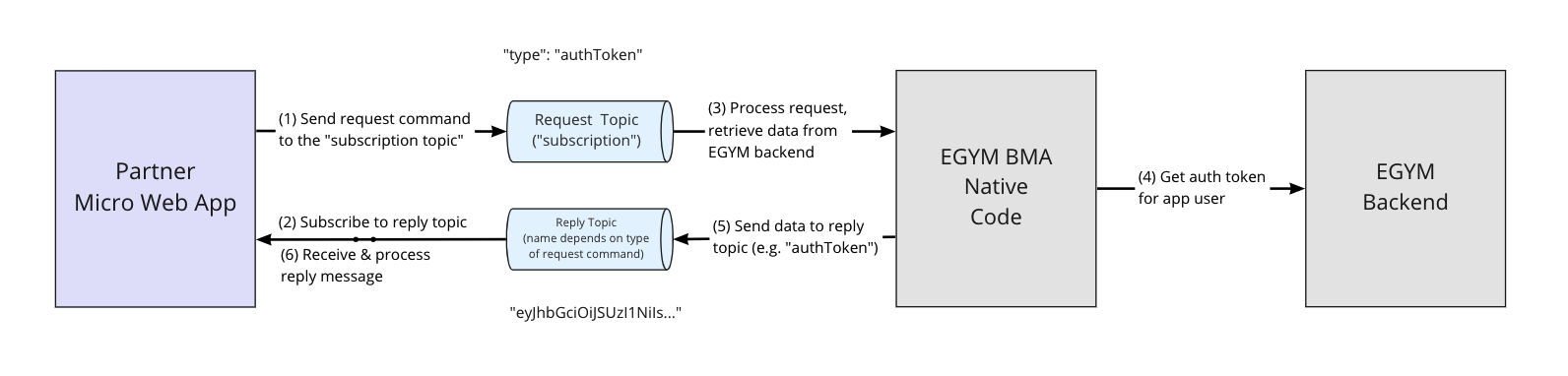
Commands sent by web application should include the following attributes:
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| type | String | Yes | Type of the request. This value also corresponds to the name of reply topic |
| data | Map | No | Additional command specific data |
It is important that every request sent by the Micro Web Application to the partner backend is secured and that it is possible to verify the identity of the user on whose behalf the request was made.
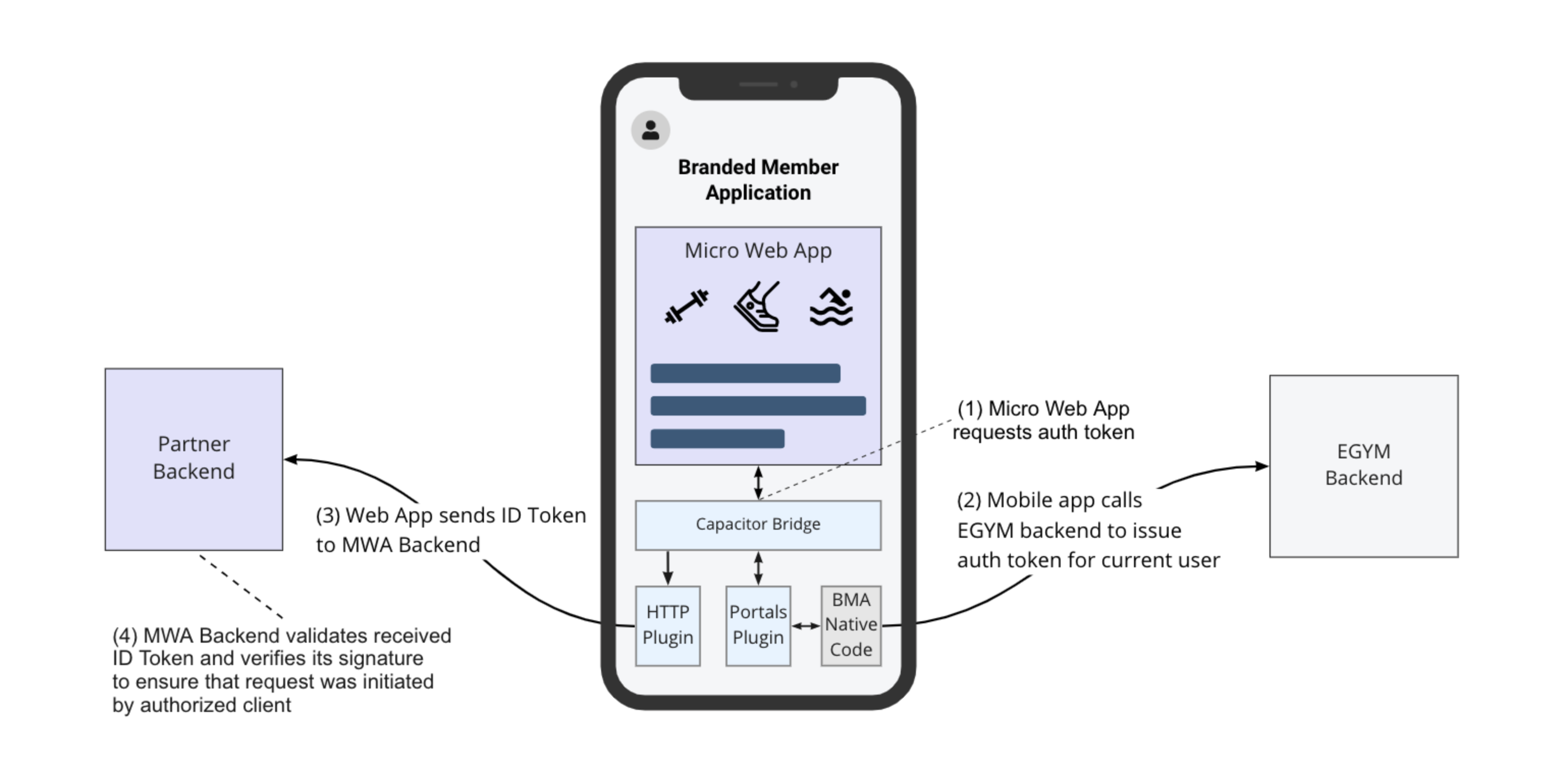
The proposed approach to do so is to use identity tokens that can be shared between EGYM and the partner system. As shown on the diagram above, the EGYM mobile app will retrieve a token for the current user from the EGYM backend and share it with the web application. The Web application will then send this token as part of a requests to its backend, and the partner backend should check the validity of the received token before any further processing of the request. Authentication tokens are initially exposed to the web application through the Initial Context, and can be also retrieved via Portals Plugin by sending the authToken command.
Tokens provided by the EGYM backend are effectively JWTs signed with the RSA algorithm. They are generated by the Firebase Authentication platform and can be verified as described below:
- Fetch public keys used to verify token signature from
https://www.googleapis.com/robot/v1/metadata/x509/securetoken@system.gserviceaccount.compublic API exposed by Firebase Authentication service - Check that token uses RS256 algorithm for computing token signature and has
kidheader which represents the identifier of one of the public keys returned from public API endpoint from previous step - Check token expiration time to ensure that token is valid
- Determine propert public key using identifier from
kidclaim and verify token signature
Please refer to Firebase Authentication Admin SDK documentation for more details.
In addition to standard JWT claims these tokens include extra user details from the EGYM platform and the gym’s membership management system
| Claim | Description |
|---|---|
| bmaUserId | Unique user identifier in BMA backend |
| egymAccountId | Identifier of user account within EGYM platform. This is an optional parameter |
| membershipId | User identifier in the gym membership system |
| gymLocationId | Identifier of exerciser’s gym within EGYM platform |
| Email used by the user for sign up or email that user provided to MMS. The value of this field is dynamic and might change between subsequent logins (user can change its email in EGYM) | |
| firstName | User first name |
| lastName | User last name |
| role | User role within EGYM platform (e.g. EXERCISER, TRAINER) |
Generated tokens have a fixed validity time set to 1 hour, so the web application might cache them internally and request new tokens from Portals Plugin once the old the one has expired.